10+ Tax Benefits With 1099 Code T
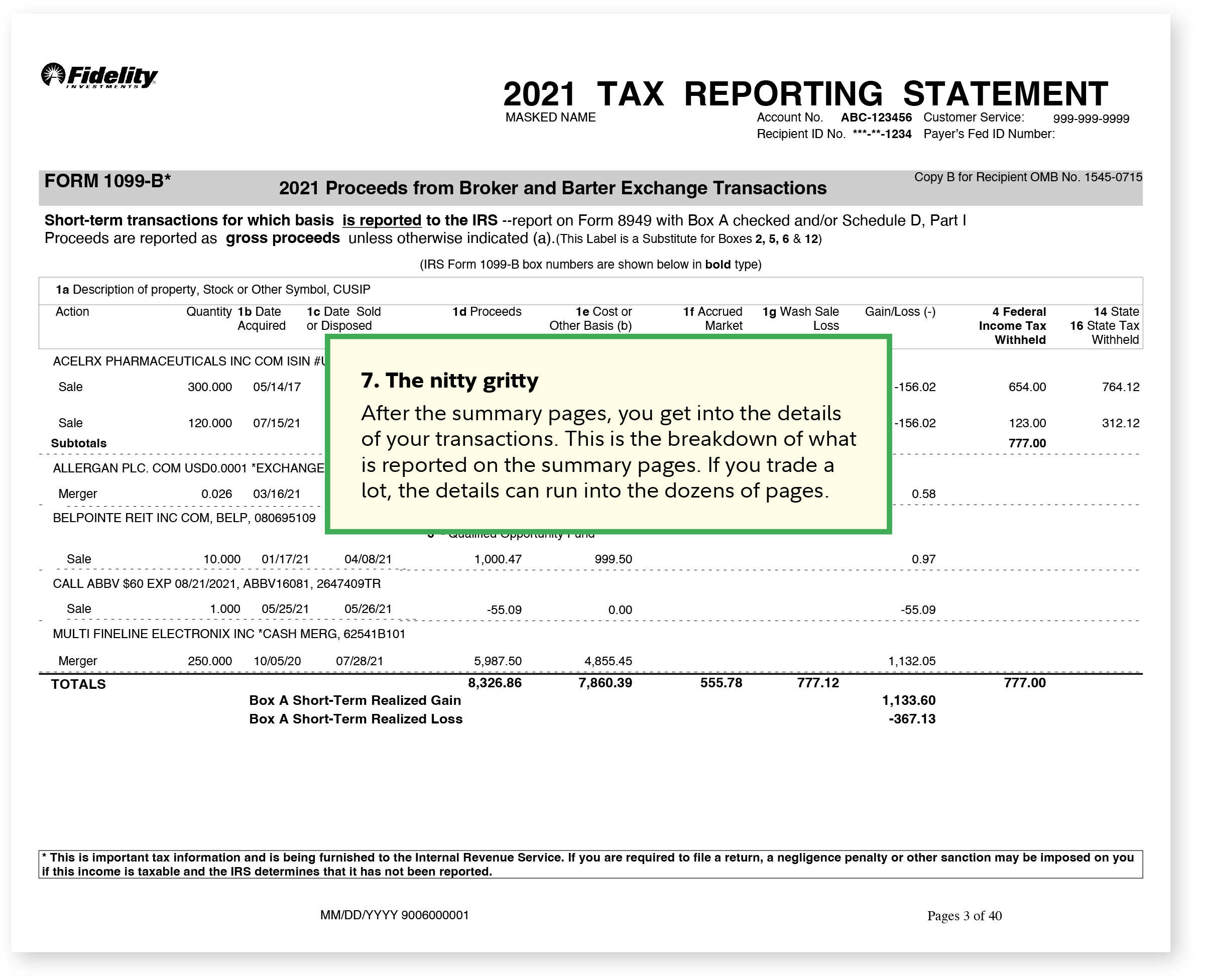
Navigating the complexities of tax benefits as a 1099 earner can be a daunting task, especially when trying to decipher the intricacies of tax codes like the 1099 code T. As an independent contractor or freelancer receiving a 1099 form, understanding these benefits is crucial for maximizing your deductions and minimizing your tax liability. The 1099 code T specifically pertains to the reporting of certain types of income, and being aware of how it impacts your tax situation can be highly beneficial. Here’s an exploration of over 10 tax benefits that you might be eligible for, along with insights into how the 1099 code T plays into your overall tax strategy.
1. Home Office Deduction
One of the most significant deductions for 1099 earners is the home office deduction. If you use a portion of your home regularly and exclusively for business, you can deduct a percentage of your rent or mortgage interest and utilities as a business expense. The 1099 code T might not directly influence this deduction, but accurately recording your business income is essential for calculating the deduction amount.
2. Business Use of Your Car
If you use your car for business purposes, you can deduct the business use percentage of your car expenses, including gas, maintenance, and insurance. Keeping a log of your business miles and personal miles is crucial for this deduction. While the 1099 code T doesn’t directly impact this, ensuring you have a record of your business-related travel can help in case of an audit.
3. Travel Expenses
Travel expenses for business, such as flights, hotels, and meals, can be deducted. It’s essential to keep receipts and records to differentiate between business and personal expenses, especially since the 1099 code T involves reporting income that might be subject to these travel deductions.
4. Equipment and Supply Deductions
Any equipment or supplies used for your business can be deducted. This includes computers, software, office supplies, and any other materials necessary for your work. The 1099 code T’s focus on income reporting means you’ll need to ensure these expenses are properly documented as offsets against your income.
5. Professional Fees
Fees paid to professionals such as lawyers, accountants, and consultants for business purposes are deductible. These might include fees for setting up your business, dealing with taxes, or obtaining professional advice. The accuracy of your 1099 code T reporting can impact how these expenses are viewed in relation to your business income.
6. Meals and Entertainment
While there are limitations, meals and entertainment expenses related to your business can be deducted. Generally, you can deduct 50% of these expenses, provided they are documented and deemed necessary for your business. The income reported under the 1099 code T can influence the proportion of these expenses that are deductible.
7. Education Expenses
If you pursue education or training related to your business, these expenses can be deducted. This includes courses, workshops, and even degrees, provided they are directly related to your current or future business activities. The 1099 code T’s emphasis on accurate income reporting can affect how these expenses are treated for tax purposes.
8. Health Insurance Premiums
As a 1099 earner, you may be able to deduct your health insurance premiums for yourself and your family. This can be a significant deduction, especially for those with high premium costs. The income level reported on your 1099 form, including code T, can impact your eligibility for certain health insurance premium deductions.
9. Retirement Plan Contributions
Contributions to a SEP-IRA or a solo 401(k) can be deducted from your business income, reducing your taxable income. These plans allow for higher contribution limits than traditional IRAs, making them an attractive option for saving for retirement while also reducing your tax liability. The 1099 code T’s role in reporting your income can affect how much you can contribute to these plans.
10. Business Liability Insurance
Premiums for business liability insurance, which protects you against claims of negligence or other business-related liabilities, can be deducted. This type of insurance is crucial for many freelance and independent contractor businesses, and the cost can be offset against your income reported under the 1099 code T.
11. Business Association Fees
Membership fees for business associations, chambers of commerce, and professional organizations can be deducted. These memberships often provide valuable networking opportunities, training, and access to resources that can benefit your business. The 1099 code T’s focus on income means these expenses can help reduce your taxable income.
Conclusion
Understanding and leveraging these tax benefits can significantly impact your bottom line as a 1099 earner. The 1099 code T, while specifically related to income reporting, plays a broader role in your tax strategy by influencing how your income and expenses are viewed by the IRS. It’s essential to keep accurate records and consult with a tax professional to ensure you’re taking full advantage of the deductions available to you. By doing so, you can minimize your tax liability and maximize your business’s financial health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the 1099 code T, and how does it affect my taxes?
+The 1099 code T pertains to specific types of income reporting. It affects how your income is categorized and can impact the deductions and credits you're eligible for. Understanding its implications is key to accurate tax reporting and maximizing your benefits.
How do I calculate the home office deduction, and what records do I need?
+To calculate the home office deduction, determine the percentage of your home used for business and apply it to your rent or mortgage interest, utilities, and other related expenses. Keep detailed records of your space measurement, rent/mortgage statements, and utility bills to support your deduction.
Can I deduct business use of my car if I also use it personally?
+Yes, you can deduct the business use percentage of your car expenses. Keep a log of your business miles and personal miles to calculate the deductible amount. You can use the standard mileage rate or actual expenses, whichever is more beneficial.
How do I differentiate between business and personal travel expenses for tax purposes?
+Keep detailed records of your trips, including receipts, itineraries, and logs of business activities. For mixed-purpose trips, allocate expenses based on the primary purpose of the trip and keep evidence to support your business expense claims.
By thoroughly understanding these tax benefits and how they interact with the 1099 code T, you can navigate the complex world of freelance and independent contractor taxes with confidence, ensuring you retain as much of your hard-earned income as possible.

