12 Stanford Marine Biology Facts To Boost Knowledge
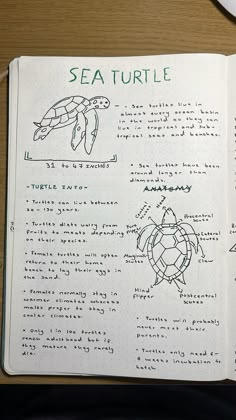
The world of marine biology is a fascinating and complex field that has captivated human imagination for centuries. With the rapid advancement of technology and scientific research, our understanding of the marine ecosystem has grown exponentially. Located on the shores of California, Stanford University has been at the forefront of marine biology research, providing groundbreaking insights into the workings of our oceanic world. Here are 12 Stanford marine biology facts that will boost your knowledge and appreciation for the intricate relationships within our planet’s marine ecosystems.
1. Diverse Marine Life
Stanford researchers have highlighted the incredible diversity of marine life, from the simplest plankton to the complex ecosystems found in coral reefs. This diversity is not just in the number of species but also in the genetic diversity within species, which is crucial for the resilience of marine ecosystems.
2. Climate Change Impact
Studies conducted by Stanford marine biologists have shown the profound impact of climate change on marine ecosystems. Rising ocean temperatures, acidification, and changes in ocean currents are affecting marine life in profound ways, from altering migration patterns to causing coral bleaching.
3. Marine Protected Areas (MPAs)
Research at Stanford has emphasized the importance of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) in conserving marine biodiversity. MPAs are designated areas where human activities are limited to protect the marine environment. Stanford studies have shown that these areas can significantly improve the health of marine ecosystems and the fisheries that depend on them.
4. Ocean’s Role in Carbon Cycle
Stanford scientists have contributed significantly to our understanding of the ocean’s role in the global carbon cycle. The ocean absorbs a substantial amount of CO2 from the atmosphere, which helps mitigate the effects of global warming but also leads to ocean acidification. This research underscores the complex relationship between the ocean and climate change.
5. Deep-Sea Exploration
Stanford has been involved in deep-sea exploration, shedding light on the mysterious ecosystems found in the deep ocean. These areas are home to unique species that have adapted to extreme conditions, such as high pressure and low light. Discoveries in these regions have expanded our understanding of biodiversity and the potential for new species discoveries.
6. Marine Policy and Conservation
The university has a strong focus on marine policy and conservation, recognizing that scientific research must be translated into action to protect marine ecosystems. Stanford researchers work closely with policymakers, NGOs, and local communities to develop and implement effective marine conservation strategies.
7. Sustainable Fishing Practices
Stanford marine biologists have worked on promoting sustainable fishing practices. This includes research on the impacts of different fishing methods, the development of more selective fishing gear, and the implementation of catch limits to prevent overfishing. Sustainable fishing is crucial for maintaining healthy fish populations and the livelihoods of people who depend on fishing.
8. Ocean Health and Human Health
There is a growing body of research at Stanford exploring the link between ocean health and human health. This includes the impact of marine pollution on human wellbeing, the role of the ocean in providing medicines, and the importance of marine ecosystems in supporting human nutrition, especially in coastal communities.
9. Advanced Technologies in Marine Research
Stanford has embraced advanced technologies such as autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), satellite imaging, and genetic sequencing to study marine ecosystems. These technologies allow for more detailed and extensive data collection than ever before, enabling scientists to ask new questions and gain insights into marine biology that were previously inaccessible.
10. Collaborative Research Initiatives
The university is involved in numerous collaborative research initiatives with other institutions, governments, and private organizations. This collaborative approach is essential for tackling the global challenges facing marine ecosystems, as it allows for the sharing of resources, expertise, and data on a scale that individual institutions cannot achieve alone.
11. Educational Programs in Marine Biology
Stanford offers a range of educational programs in marine biology, from undergraduate to graduate levels. These programs are designed not only to educate the next generation of marine biologists but also to inspire a broader appreciation and understanding of marine ecosystems among the general public.
12. Interdisciplinary Approach to Marine Biology
Stanford’s approach to marine biology is inherently interdisciplinary, combining insights from biology, ecology, chemistry, physics, policy, and social sciences. This holistic approach recognizes that marine ecosystems are complex systems influenced by a multitude of factors, and addressing the challenges they face requires a comprehensive understanding of these interactions.
Conclusion
These Stanford marine biology facts highlight the breadth and depth of research and education in this field. From the intricate details of marine life to the broad impacts of human activity on the ocean, Stanford University continues to play a pivotal role in advancing our knowledge and stewardship of marine ecosystems. As we move forward in an era marked by significant environmental challenges, the work being done at Stanford and similar institutions around the world will be essential in guiding our efforts to protect the marine world for future generations.
What is the significance of marine protected areas in conservation efforts?
+Marine protected areas are crucial for conserving marine biodiversity. They provide a safe haven for species to thrive without the pressures of human activities such as fishing and pollution. Research has shown that MPAs can lead to significant increases in biomass and biodiversity, making them a key tool in marine conservation efforts.
How does climate change affect marine ecosystems?
+Climate change has a profound impact on marine ecosystems. Rising sea temperatures can cause coral bleaching, alter species migration patterns, and affect the distribution and abundance of marine life. Additionally, ocean acidification, caused by the absorption of CO2, can hinder the ability of certain organisms, like corals and shellfish, to build their shells and skeletons, further threatening marine biodiversity.
What role does Stanford University play in marine biology research?
+Stanford University is at the forefront of marine biology research, contributing significantly to our understanding of marine ecosystems, the impacts of human activities on these ecosystems, and the development of conservation and management strategies. Through its research, educational programs, and collaborative initiatives, Stanford plays a pivotal role in advancing marine biology and informing policy and practice in marine conservation.

