8 Celsius Fahrenheit
The relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit is a fundamental concept in temperature measurement. To understand this relationship, it’s essential to delve into the history and mathematical conversion between these two scales.
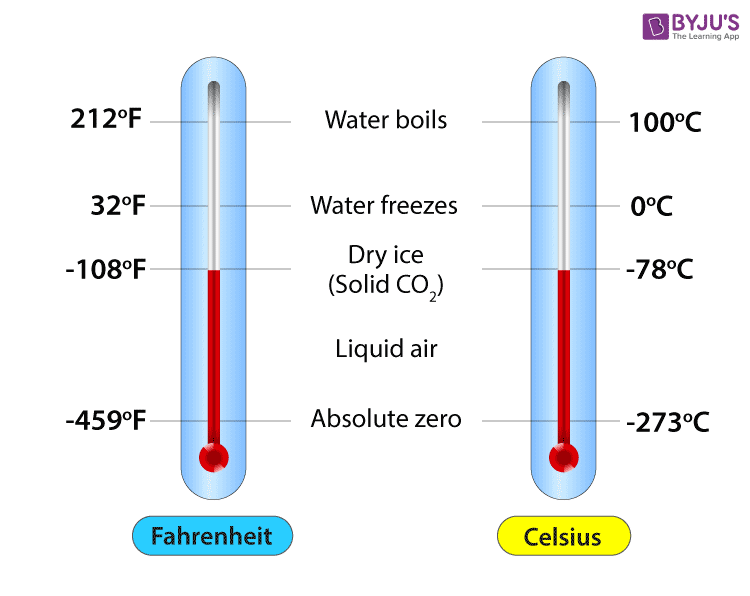
The Celsius scale, formerly known as the centigrade scale, is based on the freezing and boiling points of water. It was developed by Anders Celsius, a Swedish astronomer, in 1742. In the Celsius scale, water freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees. This scale is widely used in scientific and everyday applications due to its simplicity and logical structure.
On the other hand, the Fahrenheit scale was introduced by Gabriel Fahrenheit, a German physicist, in 1724. The Fahrenheit scale has a more complex definition, with water freezing at 32 degrees and boiling at 212 degrees. Although it was widely used in the past, especially in the United States, it has largely been replaced by the Celsius scale in most scientific and international contexts.
Now, let’s discuss the conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit. The formula to convert Celsius to Fahrenheit is: °F = (°C × 9⁄5) + 32. Conversely, to convert Fahrenheit to Celsius, the formula is: °C = (°F - 32) × 5⁄9.
Using this conversion formula, we can calculate the equivalent of 8 degrees Celsius in Fahrenheit. Plugging the value into the formula gives us: °F = (8 × 9⁄5) + 32 = (72⁄5) + 32 = 14.4 + 32 = 46.4 degrees Fahrenheit.
Understanding the Conversion Process
The conversion between Celsius and Fahrenheit involves a simple linear transformation. This means that the difference between two temperatures in one scale is proportional to the difference in the other scale, albeit with a different constant of proportionality.
To further understand the conversion, let’s consider the reference points: - The freezing point of water is 0°C or 32°F. - The boiling point of water is 100°C or 212°F.
These reference points can help in establishing a proportional relationship between the two scales.
Practical Applications of Temperature Scales
Both Celsius and Fahrenheit scales find applications in different areas. The Celsius scale, due to its simplicity and logical structure, is preferred in most scientific and international applications. It’s widely used in weather forecasting, cooking, and scientific experiments.
The Fahrenheit scale, although less commonly used today, still has its place, particularly in the United States. It’s often used in everyday applications such as weather forecasts and cooking recipes.
Conversion in Real-Life Scenarios
In real-life scenarios, converting between Celsius and Fahrenheit can be crucial for various purposes. For instance, if you’re traveling from a country that uses Celsius to one that uses Fahrenheit, understanding the conversion can help you better comprehend weather forecasts or cooking instructions.
Moreover, in scientific research, precise temperature control and measurement are critical. Here, the ability to convert between temperature scales accurately is essential for comparing data and ensuring consistency across different studies.
Exploring Other Temperature Scales
Besides Celsius and Fahrenheit, there are other temperature scales, including the Kelvin and Rankine scales. These scales are used in specific contexts, particularly in scientific and engineering applications. The Kelvin scale, for example, is an absolute temperature scale, meaning it has a theoretical zero point (absolute zero), which is crucial for thermodynamic calculations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the relationship between Celsius and Fahrenheit is essential for a wide range of applications, from scientific research to everyday life. The conversion formulas provide a straightforward method to switch between these two scales. By grasping these concepts, individuals can better navigate the complexities of temperature measurement and apply their knowledge in practical situations.
What is the main difference between the Celsius and Fahrenheit temperature scales?
+The main difference lies in their reference points and the size of their degrees. The Celsius scale sets the freezing point of water at 0 degrees and the boiling point at 100 degrees, while the Fahrenheit scale sets these points at 32 degrees and 212 degrees, respectively.
How do I convert 30 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit?
+To convert 30 degrees Celsius to Fahrenheit, use the formula: °F = (°C × 9/5) + 32. Substituting the value gives: °F = (30 × 9/5) + 32 = 54 + 32 = 86 degrees Fahrenheit.
What are the advantages of using the Celsius scale over the Fahrenheit scale?
+The Celsius scale has several advantages over the Fahrenheit scale, including its simplicity and logical structure, which makes it easier to understand and apply. Additionally, it is based on the freezing and boiling points of water, making it a more intuitive system for everyday and scientific use.
By understanding and applying the concepts related to temperature scales, individuals can enhance their ability to work with and understand temperature measurements, facilitating more effective communication and calculation across different contexts.


