Badminton Serve Rule
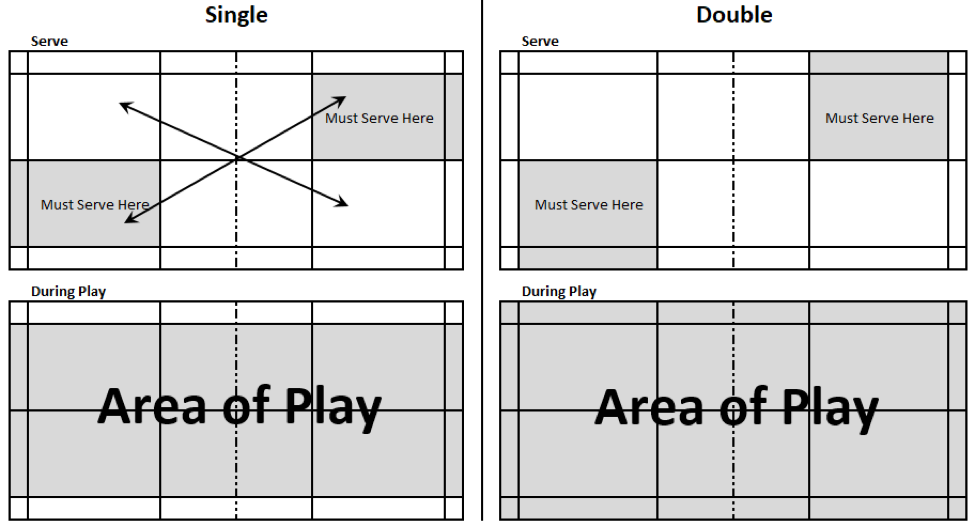
The serve is a crucial aspect of badminton, and understanding the rules surrounding it is essential for players of all levels. The badminton serve rule is designed to ensure a fair and consistent start to each rally, and it’s fascinating to explore the intricacies of this rule.
To begin with, a badminton serve is considered valid if the server hits the shuttlecock in a way that it clears the net and lands in the opponent’s court. Sounds simple, but there are several key elements to consider. Firstly, the server must stand behind the right service line, with both feet on the floor. The server’s feet must not touch the service line or extend beyond it until the serve is made.
One of the most critical aspects of the serve is the contact point between the server’s racket and the shuttlecock. The server must hit the shuttlecock below the waist, and the racket must be in a downward motion at the point of contact. This ensures that the serve is not too powerful or deceptive, giving the receiver a fair chance to return it.
The badminton serve rule also specifies that the server must not make any undue delays between points. The server has 5 seconds to make the serve after the previous point has been awarded, and any delays beyond this time limit can result in a fault being called. Furthermore, the server is not allowed to pretend to serve or make any fake serving motions, as this can be considered a distraction or an attempt to deceive the receiver.
Another important aspect of the serve is the concept of a “let” call. If the shuttlecock hits the net but still lands in the opponent’s court, it is considered a valid serve, and play continues. However, if the shuttlecock hits the net and lands outside the opponent’s court, or if it hits the net and the server faults, a “let” call is made, and the serve is replayed.
In addition to these rules, there are also specific regulations surrounding faults and lets. A fault occurs when the server hits the shuttlecock into the net, or when it lands outside the opponent’s court. A let, on the other hand, is called when the shuttlecock hits the net but still lands in the opponent’s court, or when there is an external disturbance that affects the play.
To illustrate the complexities of the badminton serve rule, let’s consider a few scenarios. Suppose a server hits the shuttlecock with the top of their racket, rather than the face. This would be considered a fault, and the server would be given another opportunity to make the serve. Alternatively, if the server hits the shuttlecock in a way that it clears the net but lands outside the opponent’s court, a fault would be called, and the server would lose the point.
In terms of strategy, the serve is a critical aspect of badminton, and players can use various techniques to gain an advantage. For example, a player may use a short serve to catch their opponent off guard, or a long serve to push their opponent back and create space. The serve can also be used to target specific areas of the opponent’s court, such as the backhand or forehand side.
A key aspect of the badminton serve rule is the importance of consistency and fairness. The rules are designed to ensure that each serve is made in a consistent and predictable manner, giving the receiver a fair chance to return it. By understanding and following these rules, players can develop a strong serve that is both effective and respectful of their opponents.
In conclusion, the badminton serve rule is a complex and nuanced aspect of the game, with multiple rules and regulations governing the serve. By understanding these rules and practicing different serving techniques, players can develop a strong and effective serve that gives them a competitive edge on the court.
What is the purpose of the badminton serve rule?
+The purpose of the badminton serve rule is to ensure a fair and consistent start to each rally, giving the receiver a fair chance to return the serve.
What is considered a valid serve in badminton?
+A serve is considered valid if the shuttlecock clears the net and lands in the opponent's court, and the server has followed the rules governing the serve.
What is the difference between a fault and a let in badminton?
+A fault occurs when the server hits the shuttlecock into the net, or when it lands outside the opponent's court. A let, on the other hand, is called when the shuttlecock hits the net but still lands in the opponent's court, or when there is an external disturbance that affects the play.
Overall, the badminton serve rule is an essential aspect of the game, and understanding its intricacies can help players develop a strong and effective serve. By following the rules and practicing different techniques, players can gain a competitive edge and improve their overall game.

