Electronic Control Throttle System
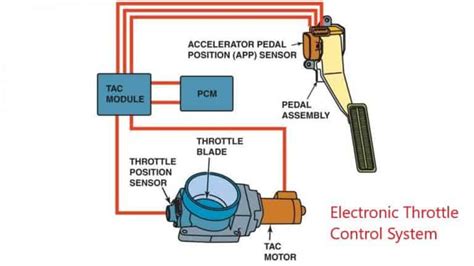
The Electronic Control Throttle System, also known as Electronic Throttle Control (ETC), is a critical component in modern vehicles that has revolutionized the way drivers interact with their cars. This innovative system has replaced traditional mechanical throttle linkages with electronic sensors and actuators, providing a more precise, efficient, and reliable way to control engine speed.
History of Electronic Throttle Control
The concept of electronic throttle control dates back to the 1980s, when automotive manufacturers began exploring ways to improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance driver comfort. The first electronic throttle control systems were introduced in the early 1990s, but they were relatively simple and prone to faults. Over the years, advancements in sensor technology, computer processing power, and software development have enabled the creation of more sophisticated and reliable ETC systems.
How Electronic Throttle Control Works
The Electronic Control Throttle System consists of several key components:
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS): This sensor measures the driver’s input on the accelerator pedal and sends an electrical signal to the Engine Control Unit (ECU).
- Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor: This sensor monitors the pedal’s position and movement, providing additional data to the ECU.
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU): The ECU processes data from the TPS, accelerator pedal position sensor, and other sensors to determine the desired engine speed.
- Throttle Actuator: This actuator adjusts the throttle valve to control airflow into the engine, based on the ECU’s calculations.
The ECU uses complex algorithms to interpret the driver’s input, taking into account factors such as:
- Driver intent: The ECU analyzes the driver’s behavior, including accelerator pedal movement, braking, and gear shifting, to determine their intended actions.
- Engine operating conditions: The ECU considers engine speed, load, temperature, and other parameters to optimize performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions.
- Vehicle dynamics: The ECU monitors the vehicle’s speed, acceleration, and deceleration to adjust the throttle response accordingly.
Advantages of Electronic Throttle Control
The Electronic Control Throttle System offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved fuel efficiency: By precisely controlling engine speed and airflow, ETC systems can optimize fuel consumption and reduce emissions.
- Enhanced performance: ETC enables faster throttle response, smoother acceleration, and more precise control over engine speed.
- Increased reliability: Electronic throttle control systems are less prone to mechanical failures and require less maintenance than traditional throttle linkages.
- Better driver comfort: ETC systems can provide a more comfortable driving experience by reducing throttle jitter, hesitation, and other undesirable phenomena.
Common Issues with Electronic Throttle Control
While Electronic Throttle Control systems are generally reliable, they can be susceptible to certain issues, such as:
- Faulty throttle position sensors: A malfunctioning TPS can cause erratic throttle behavior, hesitation, or stalling.
- ECU software issues: Software glitches or outdated calibration can lead to problems with throttle response, engine performance, or fuel efficiency.
- Throttle actuator faults: A faulty throttle actuator can cause the engine to run rough, stall, or exhibit poor performance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Electronic Control Throttle System is a sophisticated technology that has transformed the way vehicles respond to driver input. By providing precise control over engine speed, ETC systems offer improved fuel efficiency, enhanced performance, and increased reliability. While common issues can arise, proper maintenance, software updates, and troubleshooting can help ensure the optimal functioning of these systems.
FAQ Section
What is the main advantage of Electronic Throttle Control over traditional mechanical throttle linkages?
+The main advantage of Electronic Throttle Control is its ability to provide more precise and efficient control over engine speed, resulting in improved fuel efficiency, performance, and reliability.
Can Electronic Throttle Control systems be repaired or maintained?
+Are Electronic Throttle Control systems prone to faults or failures?
+While Electronic Throttle Control systems are generally reliable, they can be susceptible to faults or failures, such as faulty throttle position sensors, ECU software issues, or throttle actuator faults. Proper maintenance and troubleshooting can help minimize the risk of these issues.
Step-by-Step Guide to Troubleshooting Electronic Throttle Control Issues
Step 1: Identify the symptoms

Determine the specific issue you are experiencing, such as erratic throttle behavior, hesitation, or stalling.
Step 2: Check the throttle position sensor

Inspect the TPS for any signs of damage, corrosion, or wear. Clean or replace the sensor as needed.
Step 3: Update ECU software
Ensure the ECU software is up-to-date, as outdated calibration can cause issues with throttle response or performance.
Step 4: Inspect the throttle actuator
Check the throttle actuator for any signs of wear, damage, or malfunction. Replace the actuator if necessary.
Step 5: Consult a professional mechanic

If the issue persists after troubleshooting, consult a professional mechanic for further diagnosis and repair.
By following these steps and understanding the principles of Electronic Throttle Control, drivers and mechanics can better appreciate the complexity and sophistication of modern vehicle systems.
