Emt Soap Note Example: Master Patient Reporting
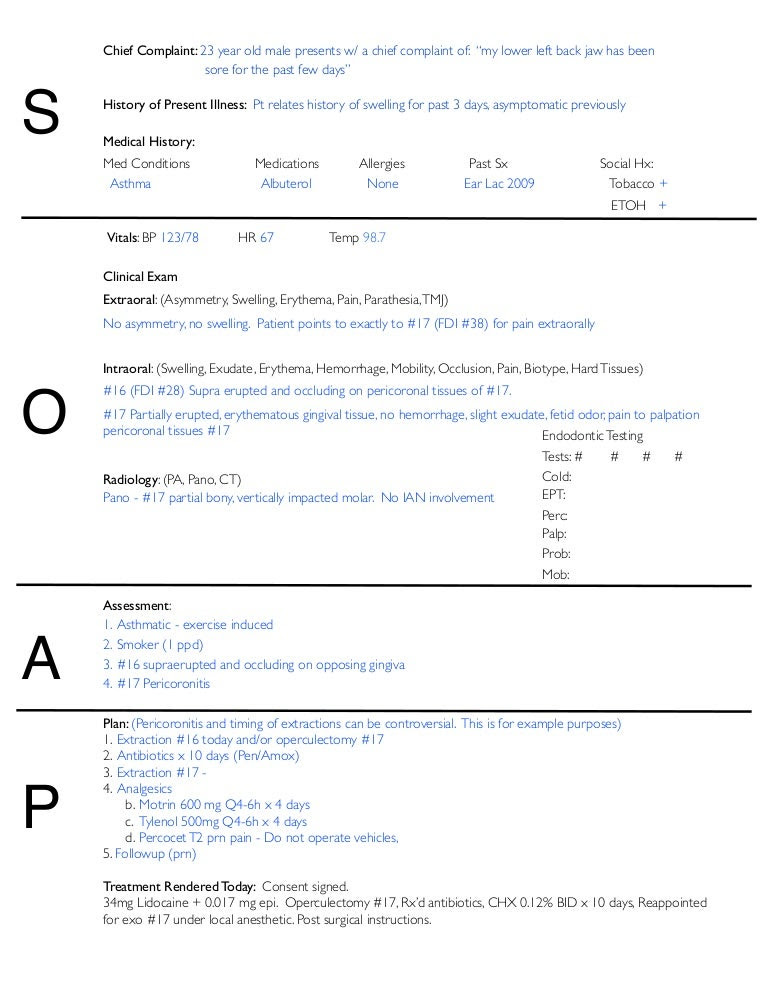
When it comes to managing patient data effectively, especially in emergency medical services (EMS) or clinical settings, the use of standardized reporting formats is crucial. One such format is the SOAP note, which stands for Subjective, Objective, Assessment, and Plan. This note-taking method is widely used in healthcare for documenting patient interactions. For Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) and other healthcare professionals, mastering the SOAP note is essential for clear, concise communication and continuity of care. Here, we’ll delve into the specifics of how to write a comprehensive SOAP note, focusing on an example related to EMT patient reporting.
Introduction to SOAP Notes
Before diving into the example, it’s essential to understand the components of a SOAP note: - Subjective: This section includes the patient’s reported symptoms, medical history, and any other relevant information that the patient or their family members provide. - Objective: This part of the note documents the objective findings, such as vital signs, physical examination results, and any diagnostic tests performed. - Assessment: Here, the healthcare provider records their diagnosis or assessment of the patient’s condition based on the information gathered in the subjective and objective sections. - Plan: The final section outlines the treatment plan, including any medications prescribed, therapies recommended, follow-up appointments, and patient education.
EMT Soap Note Example
Let’s consider an example of an EMT SOAP note for a patient involved in a motor vehicle accident:
Subjective:
The patient is a 35-year-old male who reports being involved in a two-car collision approximately 30 minutes prior to EMS arrival. He complains of neck pain and difficulty moving his left arm. He denies any loss of consciousness or other injuries. His past medical history is significant for diabetes, for which he takes metformin daily. The patient appears to be in moderate distress.
Objective:
- Vital Signs: BP 140⁄90 mmHg, HR 110 bpm, RR 24 breaths/min, O2 Sat 98% on room air, Temp 98.6°F (37°C).
- Physical Examination: The patient has limited range of motion in his left shoulder due to pain. C-spine is stabilized with a cervical collar. No other apparent injuries are noted.
- Diagnostic Tests: Field glucose check shows a blood glucose level of 180 mg/dL.
Assessment:
Based on the patient’s presentation and the information gathered, the primary assessment is for potential cervical spine injury and left shoulder injury, possibly a fracture. The patient’s diabetes is also a consideration, given his elevated blood glucose level.
Plan:
- The patient will be transported to the nearest trauma center with cervical spine stabilization in place.
- Oxygen will be administered at 2 liters per minute via nasal cannula to maintain O2 saturation above 95%.
- The patient will be given 5 mg of morphine for pain management, as his pain level is reported as 8 out of 10.
- Upon arrival at the hospital, he will undergo further evaluation, including imaging studies of the cervical spine and left shoulder.
- His blood glucose level will be monitored closely, and adjustments to his diabetes management may be necessary.
Importance of SOAP Notes in EMT Practice
SOAP notes serve as a critical tool for EMTs and other healthcare providers to communicate effectively about patient care. They ensure that all relevant information is documented and easily accessible, facilitating continuity of care and helping to prevent errors. By following the SOAP format, EMTs can provide comprehensive, structured reports that are invaluable for subsequent healthcare providers.
Best Practices for Writing SOAP Notes
- Be Clear and Concise: Ensure that the information is easy to understand and directly pertinent to the patient’s condition.
- Use Standard Terminology: Utilize medical terminology and avoid abbreviations that may be unclear to others.
- Focus on Relevant Information: Include all critical details but avoid unnecessary information that does not contribute to the patient’s care plan.
- Review and Revise: Always review the note for accuracy and completeness before finalizing it.
Conclusion
Mastering the SOAP note format is a fundamental skill for EMTs and all healthcare professionals. By structuring patient information in a clear,organized manner, these notes enhance patient care, improve communication among the healthcare team, and contribute to better patient outcomes. The example provided demonstrates how the SOAP note can be effectively applied in the field to document patient assessment and care, ensuring that patients receive the highest quality of care from the initial point of contact through to hospital admission.
FAQ Section
What is the purpose of a SOAP note in patient care?
+The primary purpose of a SOAP note is to provide a structured method of documenting patient information, ensuring clear communication among healthcare providers about the patient’s condition, treatment, and care plan.
Why is it important for EMTs to use SOAP notes?
+SOAP notes are crucial for EMTs as they provide a standardized format for reporting patient interactions, ensuring that critical information is captured and communicated effectively to subsequent healthcare providers, thereby enhancing patient care and safety.
How often should SOAP notes be reviewed and updated?
+SOAP notes should be reviewed and updated as necessary, particularly after each patient interaction or when there is a change in the patient’s condition or care plan. Regular review ensures that the information remains accurate, relevant, and useful for ongoing patient care.

