Dipole Dipole Forces Examples

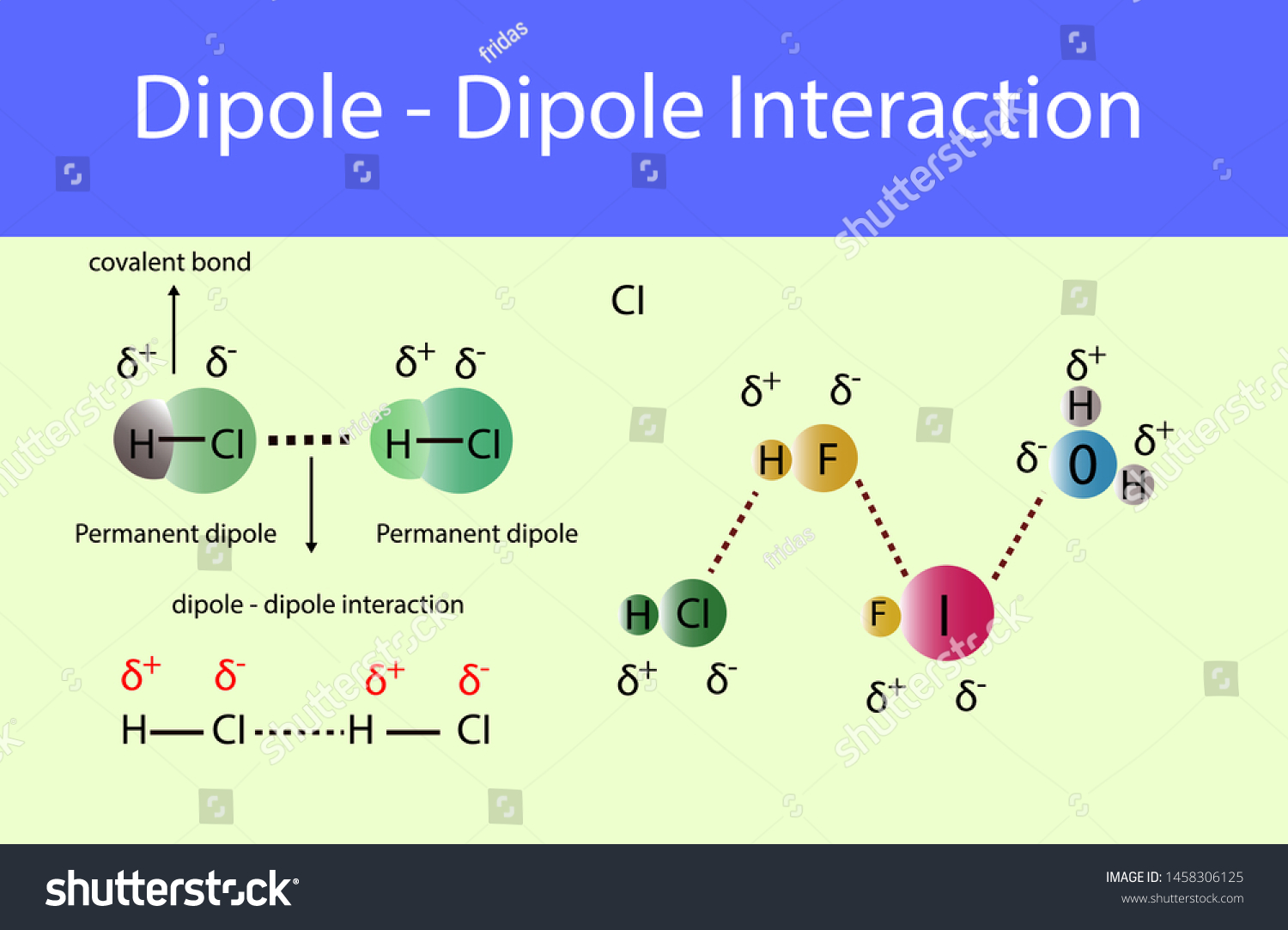
Dipole-dipole forces are a type of intermolecular force that arises between two molecules that have a permanent electric dipole moment. This permanent dipole moment occurs when a molecule has a unequal sharing of electrons between atoms, resulting in a partial positive charge on one side of the molecule and a partial negative charge on the other. The strength of dipole-dipole forces depends on the magnitude of the dipole moments and the distance between the molecules.
One of the classic examples of dipole-dipole forces is the interaction between two water molecules (H2O). Water is a polar molecule, with the oxygen atom having a partial negative charge and the hydrogen atoms having a partial positive charge. When two water molecules are brought together, the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms of one molecule is attracted to the partial negative charge on the oxygen atom of the other molecule. This attraction gives rise to a dipole-dipole force between the two molecules.
Another example of dipole-dipole forces is the interaction between two hydrogen chloride (HCl) molecules. Hydrogen chloride is a polar molecule, with the hydrogen atom having a partial positive charge and the chlorine atom having a partial negative charge. When two HCl molecules are brought together, the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom of one molecule is attracted to the partial negative charge on the chlorine atom of the other molecule, resulting in a dipole-dipole force between the two molecules.
Dipole-dipole forces also play a crucial role in the physical properties of molecules, such as their boiling and melting points. For example, the boiling point of a substance is directly related to the strength of the intermolecular forces between its molecules. Substances with stronger dipole-dipole forces, such as water and ammonia, have higher boiling points than substances with weaker dipole-dipole forces, such as methane and carbon dioxide.
In addition to these examples, dipole-dipole forces are also important in biological systems. For instance, the structure and function of proteins are influenced by dipole-dipole forces between the polar groups of amino acids. These forces help to stabilize the three-dimensional structure of proteins and play a key role in protein-ligand interactions.
The strength of dipole-dipole forces can be estimated using the following equation:
F = (μ1 * μ2) / (4 * π * ε0 * r^3)
where F is the force between the two molecules, μ1 and μ2 are the dipole moments of the two molecules, ε0 is the permittivity of free space, and r is the distance between the centers of the two molecules.
To illustrate the importance of dipole-dipole forces, let’s consider the following data:
| Molecule | Dipole Moment (D) | Boiling Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Water (H2O) | 1.85 | 100 |
| Hydrogen Chloride (HCl) | 1.08 | -85 |
| Ammonia (NH3) | 1.47 | -33 |
| Methane (CH4) | 0 | -161 |
As can be seen from the table, molecules with larger dipole moments, such as water and ammonia, have higher boiling points than molecules with smaller dipole moments, such as hydrogen chloride and methane. This is because the stronger dipole-dipole forces between molecules with larger dipole moments require more energy to overcome, resulting in higher boiling points.
In conclusion, dipole-dipole forces are an essential type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with permanent electric dipole moments. These forces play a critical role in determining the physical and chemical properties of substances, such as their boiling and melting points, and are important in biological systems. By recognizing the importance of dipole-dipole forces, we can better understand the behavior of molecules and their interactions with each other.
What is the definition of a dipole-dipole force?
+A dipole-dipole force is a type of intermolecular force that arises between two molecules that have a permanent electric dipole moment. This force is a result of the attraction between the partial positive charge on one molecule and the partial negative charge on another molecule.
What are some examples of molecules that exhibit dipole-dipole forces?
+Some examples of molecules that exhibit dipole-dipole forces include water (H2O), hydrogen chloride (HCl), and ammonia (NH3). These molecules have permanent electric dipole moments, which give rise to dipole-dipole forces between them.
How do dipole-dipole forces affect the physical properties of substances?
+Dipole-dipole forces can significantly affect the physical properties of substances, such as their boiling and melting points. Substances with stronger dipole-dipole forces, such as water and ammonia, have higher boiling points than substances with weaker dipole-dipole forces, such as methane and carbon dioxide.

