How To Charge Capacitor? Equation Guide
Charging a capacitor is a fundamental concept in electronics, and understanding the process is crucial for designing and working with various electronic circuits. A capacitor is essentially a device that stores energy in the form of an electric field. It consists of two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. When a voltage is applied across the plates, electric charge builds up on the plates, and the capacitor stores energy. The process of charging a capacitor involves applying a voltage source across it and allowing the capacitor to accumulate charge over time.
Basic Principle of Charging a Capacitor
The basic principle behind charging a capacitor is based on the movement of electrons. When a capacitor is connected to a voltage source (like a battery), electrons flow from the negative terminal of the voltage source onto one of the capacitor’s plates (making it negatively charged) and away from the other plate (making it positively charged). The dielectric material between the plates acts as an insulator, preventing the electrons from moving directly across the capacitor. As more electrons accumulate on one plate and are depleted from the other, an electric field forms between the plates.
Equation for Charging a Capacitor
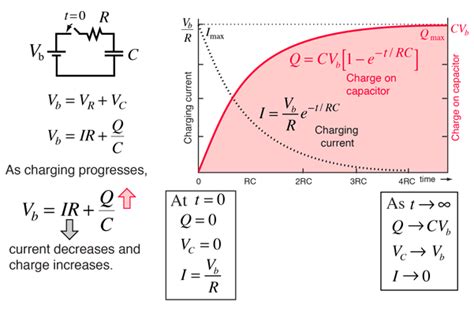
The charging process of a capacitor can be described using the RC time constant equation, where R is the resistance in the circuit, and C is the capacitance of the capacitor. The time constant (τ) of the circuit, which is the time it takes for the capacitor to charge to about 63.2% of its full capacity, is given by the equation:
τ = RC
The charge (Q) on a capacitor at any given time (t) during the charging process can be found using the equation:
Q(t) = CV(1 - e^(-t/RC))
where: - Q(t) is the charge on the capacitor at time t, - C is the capacitance of the capacitor, - V is the applied voltage, - e is the base of the natural logarithm (approximately 2.71828), - t is the time, - R is the resistance in the circuit.
This equation shows how the charge on the capacitor increases over time as it charges, approaching its maximum value (CV) as time goes to infinity.
Steps to Charge a Capacitor
Connect the Capacitor to a Voltage Source: The first step is to connect the capacitor to a voltage source, such as a battery, through a resistor. The resistor is crucial as it limits the initial surge of current and prevents damage to the capacitor or the circuit.
Allow Charging: Once connected, allow the capacitor to charge. The time it takes for the capacitor to become fully charged depends on the RC time constant of the circuit.
Monitor the Charge (Optional): Depending on the application, it might be necessary to monitor the voltage across the capacitor to determine when it has reached the desired level of charge.
Disconnect the Voltage Source: After the capacitor is charged, it can be disconnected from the voltage source. The capacitor will retain its charge until it is discharged through a circuit.
Safety Precautions
- Use Proper Voltage Ratings: Always ensure that the voltage applied to the capacitor does not exceed its rated voltage. Exceeding the voltage rating can cause the capacitor to fail or even explode.
- Handle with Care: Capacitors can store a significant amount of energy even after being disconnected from a power source. Discharge capacitors before handling them to avoid electrical shock.
- Follow Proper Discharging Techniques: Use a resistor or a discharge tool to safely discharge capacitors. Never use a wire or any conductor to short circuit a capacitor, as this can cause a spark or damage the capacitor.
Conclusion
Charging a capacitor is a fundamental process in electronics that involves applying a voltage source across the capacitor and allowing it to accumulate charge over time. Understanding the principles and equations behind capacitor charging is essential for working with electronic circuits. Always follow safety precautions and use capacitors within their rated specifications to ensure safe and effective operation.
What is the formula for the time constant of a capacitor charging circuit?
+The formula for the time constant (τ) is τ = RC, where R is the resistance in the circuit and C is the capacitance of the capacitor.
How does the charge on a capacitor change over time during charging?
+The charge (Q) on a capacitor at any given time (t) can be found using the equation Q(t) = CV(1 - e^(-t/RC)), which shows that the charge increases over time, approaching its maximum value (CV) as time goes to infinity.
Why is it important to include a resistor when charging a capacitor?
+A resistor is crucial as it limits the initial surge of current and prevents damage to the capacitor or the circuit. Without a resistor, the capacitor could charge too quickly, leading to potential damage or safety hazards.

