Rule 801 Fre

The concept of Rule 801 of the Federal Rules of Evidence is a foundational aspect of legal proceedings in the United States, specifically addressing the admissibility of hearsay evidence. To delve into the intricacies of this rule and its implications, it’s essential to understand the broader context of evidence law and the principles that guide the admission of testimony in court.
Introduction to Hearsay and Its Exceptions
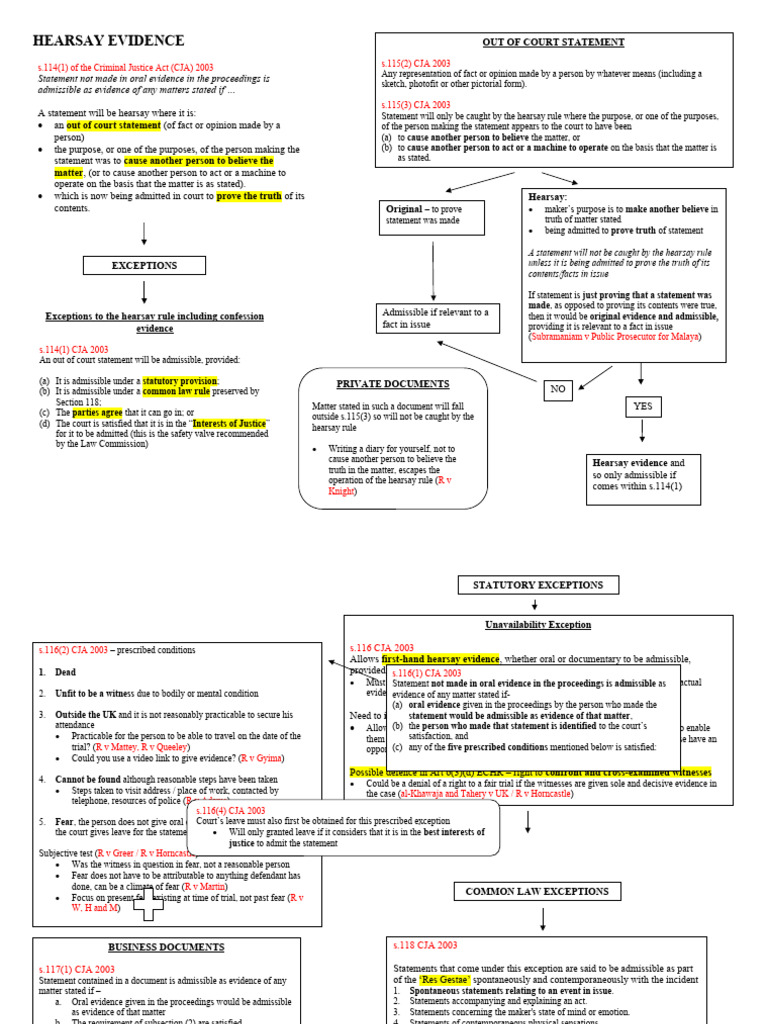
Hearsay is a statement, other than one made by the declarant while testifying at the trial or hearing, offered in evidence to prove the truth of the matter asserted. The basic rule is that hearsay is not admissible except in certain circumstances. Rule 801 of the Federal Rules of Evidence defines hearsay and outlines the general parameters for its exclusion. However, the rule also acknowledges numerous exceptions, which are critical for the admission of relevant and reliable evidence.
The Definition of Hearsay Under Rule 801

Rule 801(d) defines hearsay as a statement, other than one made by the declarant while testifying at the trial or hearing, offered in evidence to prove the truth of the matter asserted. This definition is crucial because it distinguishes between statements made for the truth of the matter asserted and those made for other purposes, such as effect on the listener. Statements made by a declarant who is testifying at the trial and available for cross-examination concerning the statement are not considered hearsay under Rule 801(d)(1).
Exceptions to the Hearsay Rule
The Federal Rules of Evidence list several exceptions to the hearsay rule under Article VIII. These exceptions include prior inconsistent statements (Rule 801(d)(1)), admissions by a party-opponent (Rule 801(d)(2)), and statements made by a declarant while perceiving an event or condition, among others. For instance, Rule 803 lists exceptions that apply regardless of the declarant’s availability to testify, such as present sense impressions, excited utterances, and statements for medical diagnosis or treatment. Rule 804 provides exceptions that apply when the declarant is unavailable, including testimony from a prior proceeding, statements under belief of imminent death, and statements of personal or family history.
Understanding the Purpose and Impact of Rule 801
The purpose of Rule 801 and the hearsay rule exceptions is to ensure that only reliable and trustworthy evidence is presented in court. By excluding hearsay evidence except under specific circumstances, the rule aims to prevent the admission of untrustworthy or misleading statements that could unfairly influence the jury. However, the numerous exceptions to the rule reflect the complexity of real-world situations and the need for flexibility in the pursuit of justice.
Practical Applications and Considerations

In practical terms, understanding Rule 801 and its exceptions is essential for legal professionals. It guides them in preparing cases, examining witnesses, and making objections to evidence during trials. The application of these rules can significantly impact the outcome of legal proceedings, as the admission or exclusion of certain statements can be pivotal in establishing facts or proving a party’s case.
Key Takeaways for Legal Professionals
- Mastering the Definitions: A clear understanding of what constitutes hearsay under Rule 801 is fundamental. Legal professionals must be able to identify hearsay and distinguish it from non-hearsay statements.
- Applying the Exceptions: Familiarity with the exceptions to the hearsay rule is crucial. This includes knowing when statements can be admitted despite being hearsay and being able to argue effectively for their inclusion or exclusion.
- Strategic Use of Hearsay Exceptions: In building a case, legal professionals must strategically consider how to use hearsay exceptions to their advantage, whether in admitting favorable evidence or excluding unfavorable testimony.
Conclusion
Rule 801 of the Federal Rules of Evidence, with its definition of hearsay and outline of exceptions, plays a critical role in shaping the contours of evidence admissible in legal proceedings. By grasping the nuances of this rule and its practical implications, legal professionals can navigate the complex landscape of evidence law more effectively, ultimately contributing to the pursuit of justice. The dynamic interplay between the exclusion of hearsay and its exceptions underscores the balancing act between ensuring the reliability of admitted evidence and allowing for the presentation of all relevant facts in a case.
FAQ Section
What is the primary purpose of Rule 801 of the Federal Rules of Evidence?
+The primary purpose of Rule 801 is to define hearsay and outline its exceptions, ensuring that only reliable evidence is admitted in legal proceedings.
What are some common exceptions to the hearsay rule under the Federal Rules of Evidence?
+Common exceptions include prior inconsistent statements, admissions by a party-opponent, present sense impressions, excited utterances, and statements for medical diagnosis or treatment.
Why are the exceptions to the hearsay rule important in legal proceedings?
+The exceptions are important because they allow for the admission of relevant and reliable evidence that might otherwise be excluded, thus facilitating a more comprehensive presentation of the facts in a case.


