Specific Heat Calculator: Fast Answers
When it comes to understanding the thermal properties of materials, specific heat capacity is a crucial parameter that defines how much heat energy is required to raise the temperature of a substance by a certain amount. This concept is vital in various fields, including physics, chemistry, and engineering, as it helps in predicting the behavior of materials under different thermal conditions. In this article, we will delve into the concept of specific heat capacity, its significance, and how a specific heat calculator can be a valuable tool for quick and accurate calculations.
Understanding Specific Heat Capacity
Specific heat capacity, often denoted as (c) or (s), is the amount of heat per unit mass required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius (or Kelvin). It is an intensive property, meaning it does not depend on the size or amount of the substance, but rather on its composition. The unit of specific heat capacity is typically joules per kilogram per degree Celsius (J/kg°C).
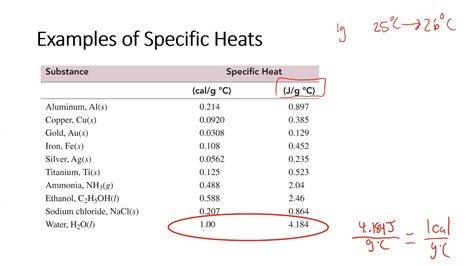
Different materials have different specific heat capacities. For example, water has a high specific heat capacity of approximately 4.184 J/g°C, which is why it can absorb and release a lot of heat energy without a large change in temperature. This property makes water an excellent coolant and explains why the oceans play a significant role in moderating Earth’s climate.
Importance of Specific Heat Capacity
The specific heat capacity of a material is crucial for various applications:
- Thermal Energy Storage: Materials with high specific heat capacities can store more thermal energy, making them useful for applications where heat needs to be stored and released, such as in solar thermal systems.
- Building Design: Understanding the specific heat capacity of building materials helps architects design buildings that are more energy-efficient by considering how different materials will absorb and release heat.
- Cooking and Food Processing: Knowledge of specific heat capacities is essential in cooking and food processing, as it determines how quickly foods heat up or cool down.
- Industrial Processes: In chemical and manufacturing processes, controlling temperature is crucial, and specific heat capacity plays a key role in designing and optimizing these processes.
Using a Specific Heat Calculator
A specific heat calculator is a tool that can quickly calculate the specific heat capacity of a substance or the amount of heat energy required to change the temperature of a given mass of a substance. These calculators are based on the formula for specific heat capacity:
[ Q = mc\Delta T ]
Where: - (Q) is the amount of heat energy transferred, - (m) is the mass of the substance, - (c) is the specific heat capacity of the substance, - (\Delta T) is the change in temperature.
To use a specific heat calculator, you typically need to input the mass of the substance, the initial and final temperatures, and sometimes the specific heat capacity of the material if you’re solving for one of these variables.
How to Choose the Right Calculator
Not all specific heat calculators are the same. Some are designed for general use, while others are tailored for specific applications, such as calculating the specific heat of gases or the thermal energy storage capacity of phase change materials. When selecting a calculator, consider the following factors:
- Accuracy and Precision: Ensure the calculator uses accurate and up-to-date values for specific heat capacities.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface can save time and reduce errors.
- Customizability: Look for calculators that allow you to input custom specific heat values or select from a wide range of materials.
- Units flexibility: A good calculator should allow you to switch between different units of measurement.
Practical Applications and Examples
Let’s consider a practical example to illustrate the use of a specific heat calculator:
Suppose you’re a chef and you need to heat 2 kilograms of water from 20°C to 80°C for cooking. The specific heat capacity of water is approximately 4.184 J/g°C. How much energy do you need to apply?
Using the formula (Q = mc\Delta T), and converting the mass of water to grams (since the specific heat capacity is given in J/g°C), we get:
[ Q = 2000 \, \text{g} \times 4.184 \, \text{J/g°C} \times (80°C - 20°C) ] [ Q = 2000 \times 4.184 \times 60 ] [ Q = 501696 \, \text{J} ]
Or, using a specific heat calculator, you could input these values directly and obtain the result.
Conclusion
Specific heat capacity is a fundamental property of materials that has wide-ranging implications across various disciplines. A specific heat calculator is an indispensable tool for anyone working with thermal energy, whether in research, engineering, cooking, or any other field where understanding heat transfer is crucial. By leveraging such calculators, professionals and hobbyists alike can make informed decisions, optimize processes, and explore new ideas with greater ease and accuracy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of specific heat capacity in everyday life?
+Specific heat capacity plays a crucial role in various aspects of everyday life, from cooking and food processing to building design and climate regulation. Its understanding helps in optimizing energy use, designing more efficient systems, and predicting material behavior under different thermal conditions.
How does specific heat capacity affect the temperature of the Earth?
+The specific heat capacity of the oceans, which cover most of the Earth's surface, has a profound effect on global climate patterns. The high specific heat capacity of water means it can absorb and release a lot of heat without large temperature changes, helping to moderate Earth's climate and weather patterns.
What are some common materials with high specific heat capacities?
+Water has one of the highest specific heat capacities among common substances, with a value of approximately 4.184 J/g°C. Other materials with high specific heat capacities include ammonia (4.70 J/g°C) and hydrogen peroxide (2.63 J/g°C). These materials are useful in applications requiring efficient thermal energy storage and transfer.
In conclusion, the understanding and application of specific heat capacity are vital across a wide range of fields, from science and engineering to everyday life. Utilizing specific heat calculators and understanding the principles behind them can enhance our ability to work with thermal energy efficiently and effectively.

