Test Electrolytes At Home
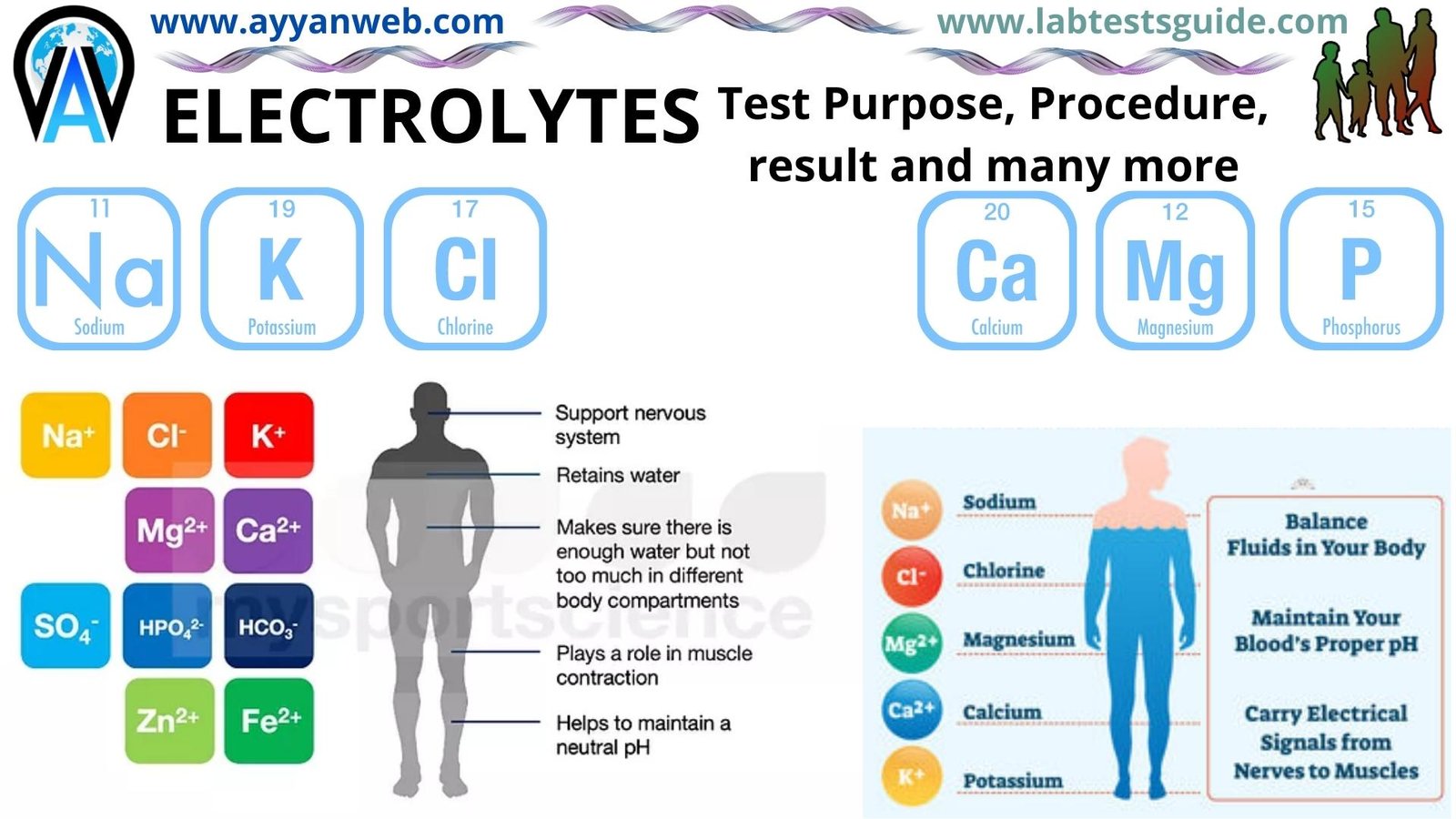
The human body is a complex system that relies on a delicate balance of various elements to function properly, and one of the key components of this balance is electrolytes. Electrolytes are electrically charged minerals that play a crucial role in various bodily functions, such as regulating the balance of fluids, maintaining proper pH levels, and enabling nerve and muscle function. The most common electrolytes in the human body are sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, and phosphate.
Testing electrolyte levels is essential to diagnose and treat various medical conditions, such as dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and kidney disorders. While electrolyte tests are typically performed in a clinical setting, there are ways to test electrolytes at home using various methods and devices. In this article, we will explore the different ways to test electrolytes at home, the benefits and limitations of home testing, and what to expect from the results.
Why Test Electrolytes at Home?
Testing electrolytes at home can be beneficial for individuals who:
- Engage in strenuous physical activities: Athletes and individuals who engage in intense physical activities may need to monitor their electrolyte levels to prevent dehydration and maintain optimal performance.
- Have underlying medical conditions: People with conditions such as kidney disease, heart failure, or certain hormonal imbalances may need to regularly monitor their electrolyte levels to manage their condition effectively.
- Experience symptoms of electrolyte imbalance: Individuals who experience symptoms such as muscle cramps, fatigue, or dizziness may want to test their electrolyte levels to determine if an imbalance is the cause.
- Want to monitor their hydration levels: Testing electrolytes at home can help individuals monitor their hydration levels and ensure they are drinking enough water to maintain proper electrolyte balance.
Methods for Testing Electrolytes at Home
There are several methods for testing electrolytes at home, including:
- Electrolyte test strips: These are small strips that change color in response to the presence of certain electrolytes in a urine or sweat sample.
- Portable electrolyte analyzers: These are handheld devices that use a small sample of blood or urine to measure electrolyte levels.
- At-home electrolyte testing kits: These kits typically include a device and test strips or cartridges that measure electrolyte levels in a urine or blood sample.
- Mobile health apps: Some mobile health apps, such as those that track hydration or athletic performance, may include features that estimate electrolyte levels based on user input and data from wearable devices.
Benefits and Limitations of Home Electrolyte Testing
Home electrolyte testing offers several benefits, including:
- Convenience: Testing electrolytes at home can save time and effort compared to visiting a healthcare provider or laboratory.
- Cost-effective: Home testing kits and devices can be more affordable than clinical tests, especially for individuals who need to monitor their electrolyte levels regularly.
- Increased awareness: Home testing can empower individuals to take a more active role in monitoring their health and making informed decisions about their well-being.
However, home electrolyte testing also has some limitations:
- Accuracy: Home testing devices and kits may not be as accurate as clinical tests, and results should be interpreted with caution.
- Limited scope: Home testing may not provide a comprehensive picture of electrolyte balance, as it may only measure a limited number of electrolytes.
- Interpretation: Home test results may require interpretation by a healthcare professional to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
What to Expect from Home Electrolyte Test Results
Home electrolyte test results can provide valuable information about an individual’s electrolyte balance, but it is essential to understand what the results mean and how to interpret them. Here are some general guidelines:
- Normal ranges: Electrolyte levels can vary depending on the individual, but general normal ranges are:
- Sodium: 135-145 mmol/L
- Potassium: 3.5-5.5 mmol/L
- Calcium: 8.5-10.5 mg/dL
- Magnesium: 1.8-2.4 mg/dL
- Chloride: 96-106 mmol/L
- Phosphate: 2.5-4.5 mg/dL
- Abnormal results: Abnormal electrolyte levels can indicate various medical conditions, such as dehydration, kidney disease, or hormonal imbalances. If home test results indicate an abnormal electrolyte level, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What are the most common electrolytes in the human body?
+The most common electrolytes in the human body are sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, and phosphate.
What are the benefits of testing electrolytes at home?
+Testing electrolytes at home can be beneficial for individuals who engage in strenuous physical activities, have underlying medical conditions, experience symptoms of electrolyte imbalance, or want to monitor their hydration levels.
How accurate are home electrolyte testing devices and kits?
+Home electrolyte testing devices and kits may not be as accurate as clinical tests, and results should be interpreted with caution. It is essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions and consult a healthcare professional if results indicate an abnormal electrolyte level.
In conclusion, testing electrolytes at home can be a convenient and cost-effective way to monitor electrolyte balance, but it is essential to understand the benefits and limitations of home testing. By choosing the right testing method and device, individuals can take a more active role in maintaining their health and well-being. However, it is crucial to remember that home test results should be interpreted with caution and in consultation with a healthcare professional to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.

