What Are Enlarged Lymph Nodes? Symptoms Guide
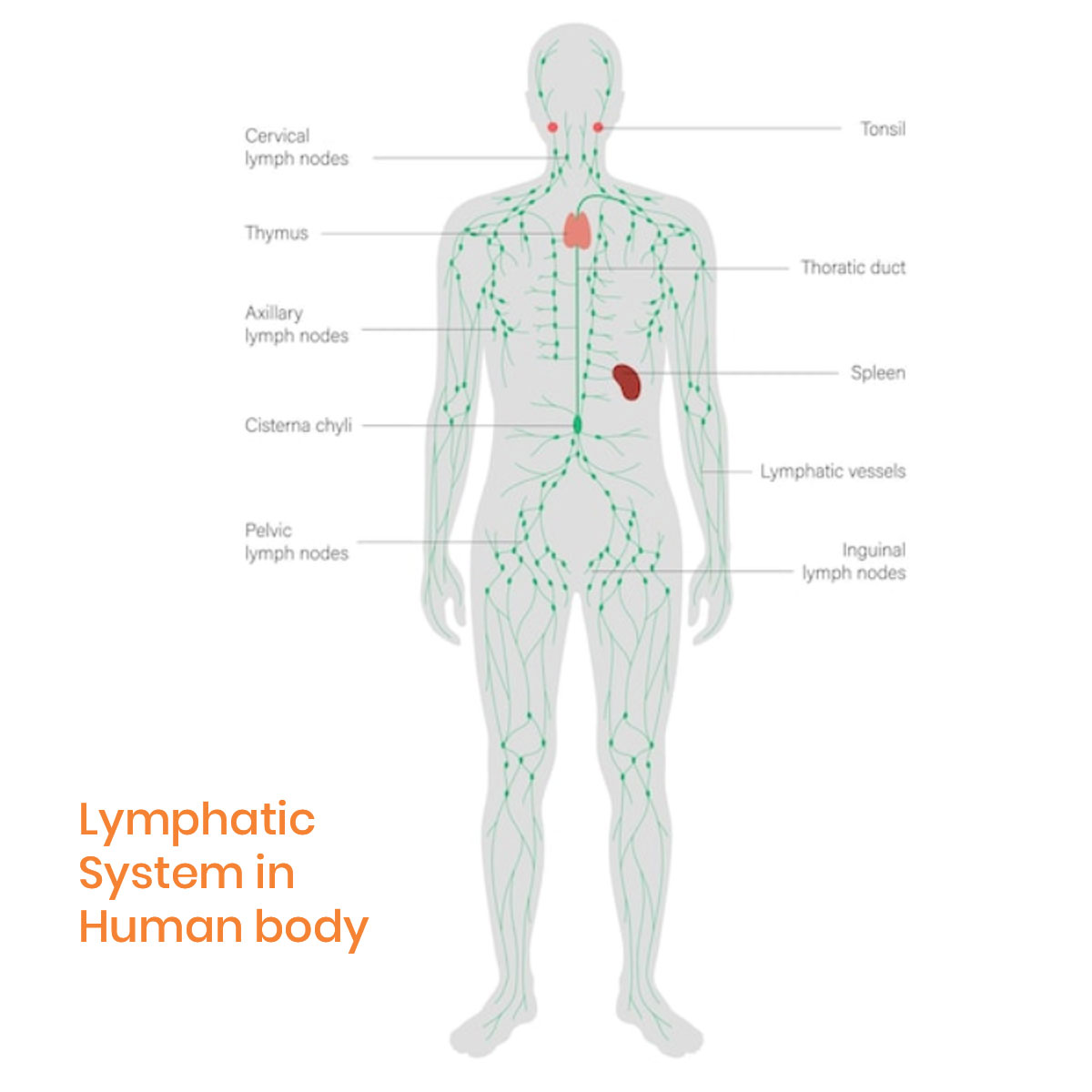
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that are part of the body’s lymphatic system, which helps to fight infection and disease. They are located throughout the body, including in the neck, armpits, groin, and behind the ears. Enlarged lymph nodes, also known as swollen lymph nodes, occur when the nodes become larger than usual, often as a result of infection, inflammation, or other medical conditions.
When lymph nodes become enlarged, it can be a sign that the body is responding to an infection or other disease process. The enlargement can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune disorders, or cancer. In some cases, enlarged lymph nodes can be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition, such as lymphoma or leukemia.
Symptoms of enlarged lymph nodes can vary depending on the location and severity of the enlargement. Some common symptoms include:
- Swelling or tenderness in the affected area
- Pain or discomfort when touching the affected area
- Redness or warmth around the affected area
- Fever or chills
- Fatigue or weakness
- Weight loss or loss of appetite
In some cases, enlarged lymph nodes can be asymptomatic, meaning that they do not cause any noticeable symptoms. However, if the enlargement is caused by an underlying infection or disease, other symptoms may be present, such as coughing, sore throat, or difficulty swallowing.
Causes of Enlarged Lymph Nodes
Enlarged lymph nodes can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Viral infections, such as mononucleosis or HIV
- Bacterial infections, such as tuberculosis or strep throat
- Autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus
- Cancer, including lymphoma, leukemia, or metastatic cancer
- Inflammatory conditions, such as sarcoidosis or Crohn’s disease
In some cases, enlarged lymph nodes can be caused by other factors, such as:
- Insect bites or stings
- Allergic reactions
- Trauma or injury to the affected area
- Certain medications or vaccines
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you are experiencing symptoms of enlarged lymph nodes, it’s essential to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause. A healthcare professional will perform a physical examination and take a medical history to help diagnose the condition.
Diagnostic tests may include:
- Blood tests to check for infection or disease
- Imaging tests, such as X-rays or CT scans, to visualize the affected area
- Biopsy to examine a sample of tissue from the affected lymph node
Treatment for enlarged lymph nodes will depend on the underlying cause. In some cases, no treatment may be necessary, and the lymph nodes will return to their normal size once the underlying condition has been treated. In other cases, treatment may include:
- Antibiotics to treat bacterial infections
- Antiviral medications to treat viral infections
- Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce swelling and pain
- Chemotherapy or radiation therapy to treat cancer
Conclusion
Enlarged lymph nodes can be a sign of an underlying infection or disease, and it’s essential to seek medical attention to determine the cause. While in many cases, enlarged lymph nodes will return to their normal size once the underlying condition has been treated, in some cases, they can be a symptom of a more serious underlying condition. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for enlarged lymph nodes, you can better manage your health and seek medical attention if necessary.
What are the most common causes of enlarged lymph nodes?
+The most common causes of enlarged lymph nodes include viral infections, such as mononucleosis or HIV, bacterial infections, such as tuberculosis or strep throat, and autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus.
How are enlarged lymph nodes diagnosed?
+Enlarged lymph nodes are diagnosed through a physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests, such as blood tests, imaging tests, and biopsy.
What are the treatment options for enlarged lymph nodes?
+Treatment options for enlarged lymph nodes depend on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics, antiviral medications, anti-inflammatory medications, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
